What is a Point Cloud?
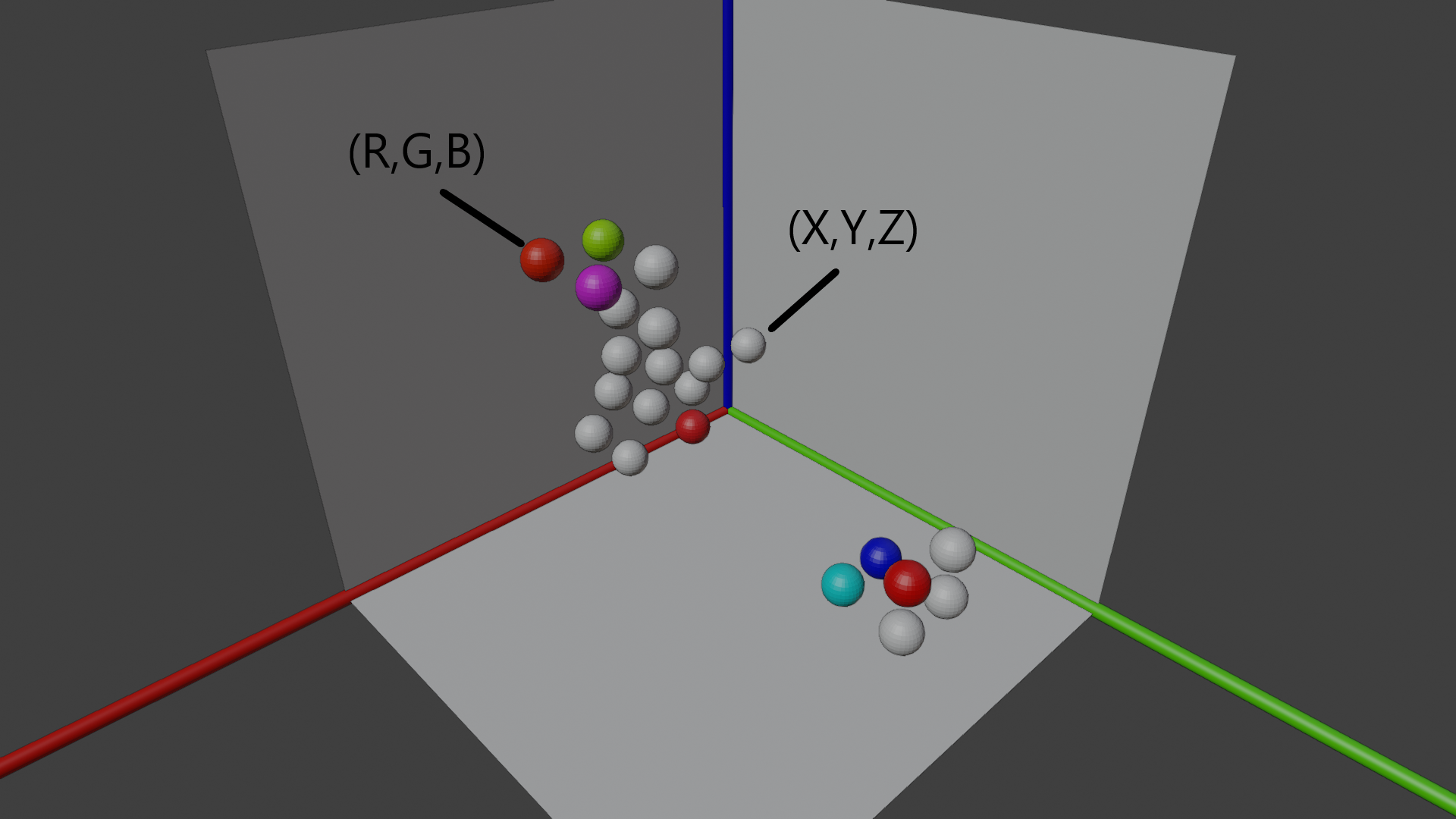
A point cloud is a collection of data points. These data points are coordinates in space. Millions, billions, or even trillions of points make up a point cloud. At its simplest, a point in a point cloud consists of a position represented by X, Y, and Z coordinates. Additionally, metadata, or attributes, can be attached to these points. For instance, the color of a point is often represented as an RGB value. Other attributes can also be included.
Since point clouds can consist of an enormous number of points, the datasets involved are typically very large. These range from small point clouds (30-80 MB), medium-sized ones (500 MB - 4 GB), to extremely large point clouds (1 TB or more). These size categories are not scientifically defined but are intended to provide a sense of the potential scale of point clouds.
Illustration of points in a small point cloud within a three-dimensional space with RGB and positional values
Where Do the Data Come From?
Since point clouds are made up of many points, the origin of these points needs to be explained. Points are generated through laser scanning or photogrammetry.
Laser Scanners emit lasers that are reflected by objects. Reflections are captured when the laser hits an object. The reflected laser changes due to various factors, the most straightforward being the distance the laser traveled. Depending on this distance, the position of the point can be determined.
Photogrammetry is a process of image processing. An object captured from one or more perspectives can be processed into a digital model through this method.
What Are Point Clouds Used For?
The main focus of point clouds is the creation of 3D models. The point cloud itself can be visualized as a 3D model. However, point clouds are often converted into polygon meshes. This might be because many are more familiar with polygon meshes (e.g., in Blender).
These models can then be used for various measurements, such as:
- Measuring distances
- Calculating areas
- Estimating volumes
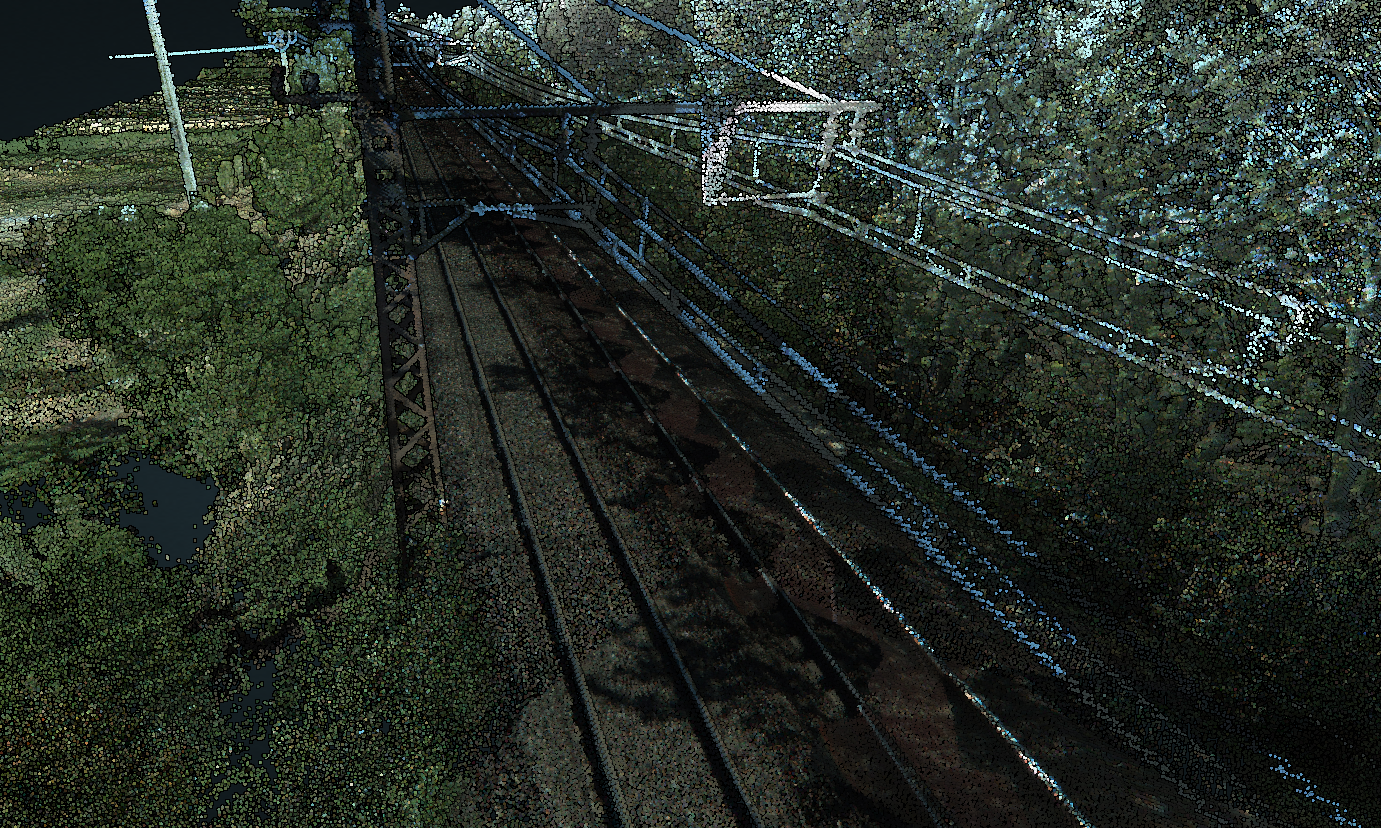
These measurements are particularly useful in fields like construction or monitoring railway tracks.
Railway track point cloud visualized in Entwine

Aarhus, Denmark point cloud visualized in Entwine
